tibial torsion test prone|how to measure tibial torsion : purchasing External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young . webNa VegasSlotsOnline encontra o mais completo catálogo de slots grátis da internet, podendo jogar em cada uma delas de forma completamente grátis e procurando por .
{plog:ftitle_list}
29 de ago. de 2018 · AP-LITE-BGAPC藻蓝蛋白荧光计由Aquameter读数表、AP-LITE传感器罩以及LITE-BGAPC藻蓝蛋白传感器三个主要部分组成,用于测量水体藻蓝蛋白含量,系统可通过GPS Aquameter现场读取和采集数据。 技术参数: Aquameter读数表: 尺寸(W*H*D):90*180*39mm. 重量(含电池):450g. 显示屏:带背光,80个字符LCD. 内 .
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of internal rotation in a patient with an in-toeing gait.External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young . Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle.
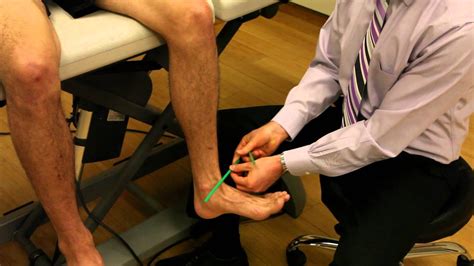
Special Test: Tibial Torsion Test PROCEDURE (Prone): knee flexed to 90°. the examiner views from above the angle formed by the foot and thigh after the subtalar joint has been placed in .
Tibial Torsion Prone Test (CR) Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures. .more. External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young children caused by abnormal external rotation of the tibia leading to an out-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle measuring greater .
Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ.
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.Internal Tibial Torsion. - Discussion: - medial rotation of the tibia at the knee causes an intoeing gait; - it is measured by the angular difference between transmalleolar axis & bicondylar axis of knee; - may result in part to excessive .To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90 °. Typically the foot axis is 10 ° .
Internal tibial torsion can be diagnosed through a physical exam and measurements of the legs. Internal Tibial Torsion Treatment. This condition usually improves without treatment by about 4 years of age. Bracing, casting and physical therapy are not usually needed. A child’s growth is closely monitored to ensure the internal tibial torsion .Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically . Create Personal Test Create Group Test . knee pain when associated with tibial torsion. awkward running style. . hip motion (tested in the prone position) increased internal rotation of >70° (normal is 20-60°) .
GENERAL INFORMATION. Active movements of the lower leg, ankle, and foot should be done in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing positions (long leg sitting or supine lying), and the examiner should note any differences, because foot deformities and deviations, in addition to decreased range of motion (ROM), can lead to injury in other parts of the lower .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (the bones that are located between the knee and the ankle). Tibial torsion causes the child's feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a "pigeon-toed" appearance. It is typically seen among toddlers. What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion can occur due to the position of the .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. . a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and foot resting in its natural position.
External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent . Tibial torsion was calculated by subtracting the proximal tibial angle from the distal tibial angle. . Continuous variables were checked for normal distribution using the Shapiro–Wilk test, and presented in the form of mean ± SD (standard deviation). . The positioning of the subjects was prone and the knee flexed to 90°, and the ankle .
External tibial torsion is usually seen between four to seven years of age. 1, 9 It is often unilateral and more common on the right side. 9 The tibia rotates laterally with growth, making lateral .Tibial torsion can happen because of the position of the baby in the uterus. It also tends to run in families. Typically, a child’s walking style looks like that of their parents. What are the symptoms of tibial torsion in a child? . Know why a test or procedure is .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child's feet to turn inward. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for .Clinical test for alignment
Side lying test of Slocum Noyes test/ Flexion rotation drawer test PMRI (Postero-medial Rotatory Instability) Medial Capsular ligament tibial collateral ligament POL ACL: PLRI (Postero-Lateral Rotatory Instability) PLC which includes LCL, Arcuate ligament complex, fabellofibular ligament, postero-lateral capsule: Dial test (prone external . Tibial torsion test in the prone position: The patient is in the prone position with the knee flexed up to 90′. The examiner views from above the angle formed by the foot & thigh after the subtalar joint has been placed in the neutral position, noting . c Second toe test: the patient is prone with the knee extended; the hip is rotated until the 2nd toe points directly towards the floor; the knee is then flexed to 90° while preventing a change in thigh rotation; the angle between the vertical and the tibial longitudinal axes is the degree of tibial torsion
Measuring femoral torsion with the trochanteric prominence angle test: With the patient prone, anteversion is measured when the greater trochanteric is palpated in its most prominent position as the hip is internally and externally rotated. . Tibial torsion – a simple clinical apparatus for its measurement and its application to a normal .External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent .Hip rotation is best examined with the patient prone, hip extended and knee flexed to 90°; the tibia and examination couch are useful reference points. . B. Measuring anteversion using the trochanteric prominence angle test (Craig’s test); C. Hip internal . abnormal tibial torsion may exacerbate foot deformities. For example, internal .
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . Normally, lateral rotation of the tibia increases from approximately 5º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity; femoral anteversion decreases from approximately 40º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity. Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing.
Purpose: To assess for rotary instability in the knee. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The tested knee should be placed in 30 degrees of flexion. The examiner then passively rotates the tibia medially and laterally (on the femur). Compare to the opposite extremity and to the opposite motion on the same leg. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . Tibial torsion is a term used to describe the physiologic twist of the distal relative to the proximal articular axis of the tibial bone in the transverse plane around its longitudinal axis . For the prone goniometric method, the patient was positioned prone, the knee on the side to be measured flexed 90°, and the ankle positioned in neutral .Rotational deformity is a less common cause of patellar instability than trochlear dysplasia and patella alta. In some cases, rotational deformity is the primary bony factor producing the instability and should be corrected surgically. More research is needed on what are normal values for femoral version and tibial torsion, as well as when the axial plane alignment needs to be .
The patient is positioned prone. Flex the knee to 90°, position the hindfoot vertically, and dorsiflex the ankle to 90° with the foot in subtalar neutral position. . The second-toe test. (A) An external tibial torsion leads to an outwardly pointed foot when the patient is relaxed in the prone position with the knee fully extended. (B) .External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent . With the patient in a prone position and the knees flexed, the TFA can be assessed by the degree of angulation of the foot towards or away from the midline. Expected variation is an angle between 10 to 15 degrees. Another method to evaluate tibial torsion is to quantify the difference between the knee axis and the transmalleolar axis.
tibial torsion special test
tibial torsion in adults
physical therapy for tibial torsion
29 de abr. de 2021 · 請記住以下網址,以便日後訪問本站。
tibial torsion test prone|how to measure tibial torsion